The complete guide to choosing and implementing the right team structure for sustainable real estate success in 2025.
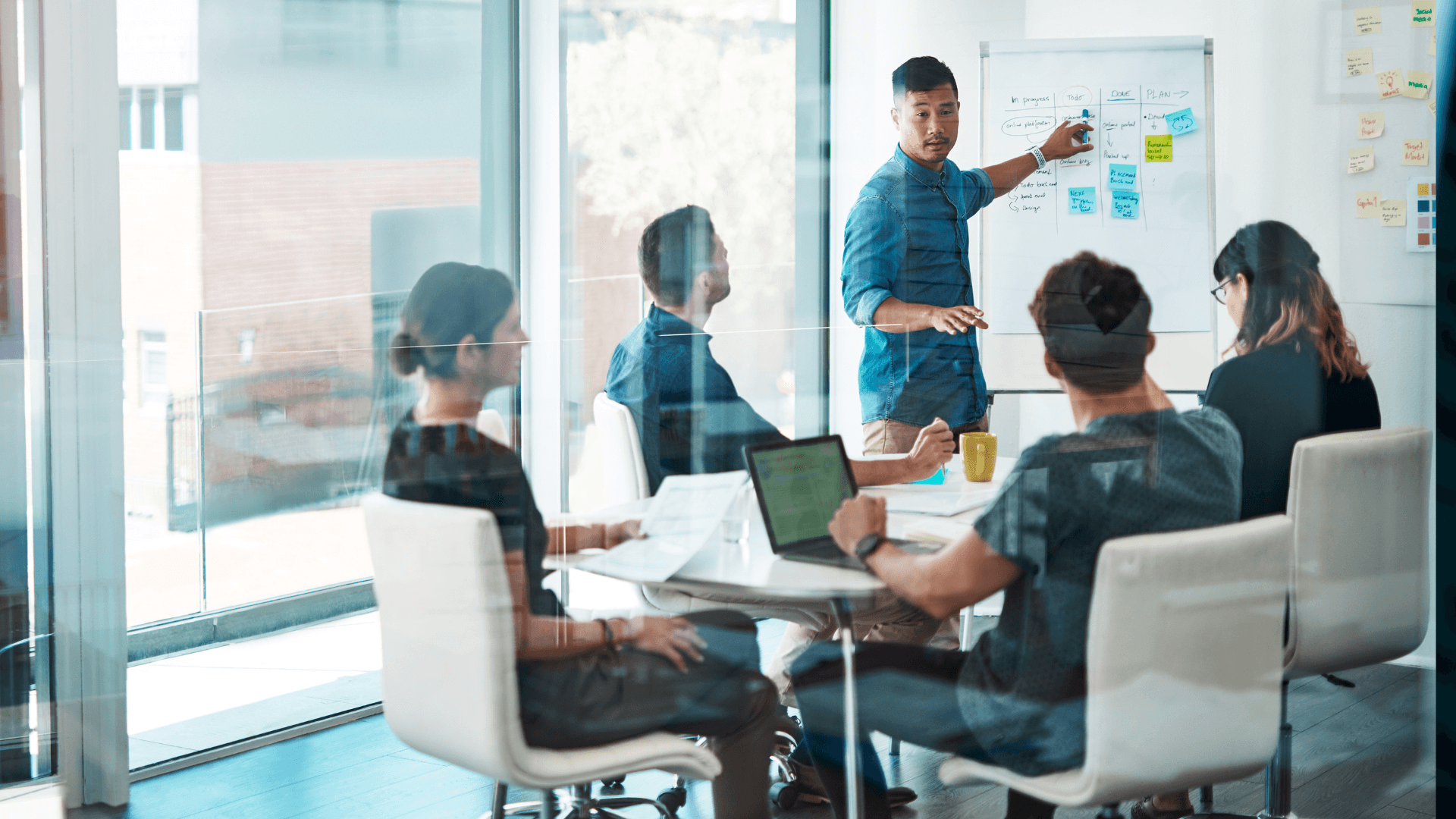
In the rapidly evolving real estate landscape, team structure isn’t just an organizational detail—it’s the foundation that determines whether your team thrives or struggles. While solo agents close an average of 12 transactions annually, well-structured real estate teams consistently achieve 87+ transactions per year with higher profit margins and better client satisfaction scores.
The difference isn’t just volume—it’s systematic efficiency. The right real estate team structure amplifies individual strengths, eliminates operational bottlenecks, and creates scalable systems that work whether you’re handling 50 transactions or 500. But with so many possible configurations, how do you choose the model that will drive results for your specific situation?
This comprehensive guide examines seven proven team structures that consistently deliver exceptional results. You’ll discover not just how each model works, but when to use them, how to implement them, and how to avoid the common pitfalls that derail even well-intentioned teams.
Why Team Structure Determines Success
The Critical Difference
Successful real estate teams don’t happen by accident—they result from intentional structural decisions that align with market realities and team capabilities. Research from the National Association of REALTORS® reveals that teams with clearly defined structures outperform loosely organized groups by 340% in revenue generation and 67% in client retention rates.
Well-structured teams also experience:
- Reduced Role Confusion Clear hierarchies and responsibilities eliminate the conflicts that plague many teams.
- Improved Client Experience Systematic handoffs and specialized expertise create smoother transactions.
- Enhanced Scalability Defined structures provide frameworks for adding team members without disrupting operations.
- Better Performance Management Clear roles enable objective evaluation and targeted improvement efforts.
How Structure Impacts Core Operations
- Productivity Multiplication The right structure ensures highly skilled agents focus on revenue-generating activities while support staff handles administrative tasks. Top-performing teams achieve 3.2× higher revenue per agent than unstructured groups.
- Client Satisfaction Enhancement Structured teams provide consistent service delivery and clear communication channels. Clients always know who to contact for specific needs, reducing frustration and improving outcomes.
- Scalability Foundation As markets change and teams grow, solid structures provide frameworks for expansion without operational chaos. Teams with defined structures can double in size while maintaining service quality.
The Foundation: Core Elements of Any Successful Team Structure
Essential Roles in Modern Real Estate Teams
Regardless of specific structure, successful teams incorporate four fundamental functions:
-
Lead Generation and Business Development Someone must consistently attract new prospects and maintain referral relationships, a role requiring dedicated time and specialized skills.
-
Client Relationship Management Building and maintaining relationships with buyers, sellers, and referral sources demands ongoing attention and personal touch.
-
Transaction Coordination and Administration Modern real estate transactions involve dozens of deadlines, documents, and coordination points. Systematic management of these details prevents costly delays and errors.
-
Marketing and Listing Management Professional photography, staging coordination, online marketing, and promotional activities require specialized knowledge and consistent execution.
Key Structural Decisions
- Hierarchy vs. Flat Organization Traditional hierarchies provide clear decision-making authority but may limit agent autonomy. Flat structures encourage collaboration but can create confusion during critical decisions.
- Specialist vs. Generalist Approaches Specialists develop deep expertise in specific areas but may create dependencies. Generalists provide flexibility but may lack depth for complex transactions.
- Geographic vs. Demographic Divisions Geographic territories leverage local knowledge but may limit growth. Demographic specializations (e.g., first-time buyers, luxury clients) develop targeted expertise but require broader market coverage.
- Commission Structures Compensation must align individual incentives with team goals while providing growth opportunities and fair recognition for contributions.
Technology Infrastructure Requirements
- Centralized Communication Systems Platforms that organize emails, documents, and communications automatically to prevent information gaps and missed deadlines.
- Collaborative CRM Platforms Systems supporting multiple users while maintaining data integrity and enabling performance tracking.
- Transaction Management Integration Platforms that coordinate multiple agents working on simultaneous transactions while maintaining compliance and deadline tracking.
Model 1: The Traditional Hierarchy Team
Structure Overview
The traditional hierarchy remains the most common team structure because it provides clear authority, accountability, and scalability:
- Team Leader/Rainmaker Focuses on business development, high-value relationships, and strategic decisions. Typically retains 40–60% of gross commission income.
- Buyer’s Agents and Listing Specialists Handle specific aspects of transactions under the leader’s guidance. Receive 25–40% commission splits.
- Administrative Support and Transaction Coordinators Non-licensed staff who manage scheduling, marketing, database maintenance, and transaction coordination.
- Clear Chain of Command Decision-making authority flows from the leader through specialists to support staff.
Best For
- Experienced Team Leaders with Strong Personal Brands
- High-Volume Transaction Markets
- Traditional Residential Sales Focus
Advantages
- Clear Accountability
- Efficient Decision-Making
- Scalable Growth
- Training and Development
Challenges
- Potential Bottlenecks
- Limited Agent Autonomy
- Succession Planning
- Revenue Concentration
Implementation Tips
- Define Clear Role Descriptions
- Establish Performance Metrics
- Create Communication Protocols
- Implement Workflow Systems
Model 2: The Partnership-Based Team
Structure Overview
Agents combine practices as equals, sharing responsibilities and rewards:
- Equal Partners with Shared Leadership
- Specialist Partnerships
- Joint Branding and Marketing
- Shared Decision-Making
Best For
- Experienced Agents with Complementary Skills
- Shared Risk Preferences
- Markets Requiring Diverse Expertise
Revenue Distribution Models
- Equal Partnership Splits
- Contribution-Based Formulas
- Performance-Weighted Distributions
Pros
- Shared Workload
- Diverse Expertise
- Risk Distribution
- Enhanced Resources
Cons
- Potential Conflicts
- Decision Delays
- Exit Complications
- Unequal Contributions
Model 3: The Specialist Pod System
Structure Overview
Large teams break into small pods (3–5 people), each focused on a market segment:
- Market Segment Specialization
- Shared Resources and Infrastructure
- Cross-Pod Collaboration
- Unified Brand with Specialized Messaging
Best For
- Large Teams Serving Diverse Markets
- Multiple Geographic Territories
- Various Price-Point Specializations
Specialization Examples
- Luxury Market Pod
- First-Time Buyer Pod
- Investment Property Pod
- Commercial Referral Pod
Coordination Requirements
- Inter-Pod Communication Systems
- Shared Document Repositories
- Unified Transaction Tracking
Model 4: The Geographic Territory Model
Structure Overview
Assign agents to specific areas for deep local expertise:
- Local Market Expertise
- Territory-Based Lead Distribution
- Regional Performance Tracking
- Community Relationship Building
Best For
- Large Metropolitan Areas
- Distinct Neighborhood Characteristics
- Teams Emphasizing Local Expertise
Territory Assignment Strategies
- Population-Based Divisions
- Transaction Volume Balancing
- Agent Experience Matching
- Market Potential Assessment
Performance Management
- Territory-Specific Metrics
- Cross-Territory Collaboration Protocols
- Centralized Reporting Systems
Model 5: The Client Lifecycle Team
Structure Overview
Organize around phases of the customer journey:
- Lead Generation Specialists
- Conversion and Showing Agents
- Transaction Management Specialists
- Client Retention Coordinators
Best For
- High-Volume Teams (200+ transactions/year)
- Conversion Optimization Focus
- Strong Lead Generation Operations
Workflow Optimization
- Systematic Handoff Procedures
- Phase-Specific Performance Tracking
- Quality Control Systems
- Automated Workflow Management
Model 6: The Hybrid Brokerage Model
Structure Overview
A mini-brokerage within a larger company:
- Individual Agent Independence
- Collaborative Resource Sharing
- Flexible Participation Levels
- Unified Brand with Individual Identity
Best For
- Experienced Agents Seeking Independence with Support
- Teams with Varying Commitment Levels
- Markets Supporting Multiple Approaches
Resource Sharing Agreements
- Marketing Cost Allocation
- Lead Distribution Protocols
- Administrative Support Sharing
- Technology Platform Access
Compliance and Oversight
- Broker Supervision Requirements
- Individual vs. Team Liability
- Performance Standards
Model 7: The Virtual/Remote Team Structure
Structure Overview
Geographically distributed members collaborate via digital tools:
- Geographically Distributed Members
- Digital-First Communication
- Shared Technology Platforms
- Flexible Work Arrangements
Best For
- Teams Serving Multiple Markets
- Work-Life Balance Emphasis
- Strong Technology Adoption
Technology Requirements
- Cloud-Based Document Management
- Video Conferencing & Collaboration
- Mobile-Optimized Systems
- Secure Communication & File Sharing
Management Considerations
- Performance Tracking & Accountability
- Team Building & Culture Maintenance
- Client Service Consistency
- Training & Development Delivery
Choosing the Right Model for Your Team
Assessment Framework
-
Current Situation Analysis
- Team size, experience, market characteristics, client base, tech capabilities.
-
Growth Goals & Timeline
-
Cultural Fit & Values
Decision Matrix Tool
- Scoring Framework
- Weighted Criteria
- Implementation Complexity
- Resource Requirement Analysis
Implementation Strategies for Each Model
Transition Planning
- Timeline Development
- Role Redefinition
- Communication Strategies
- Workflow System Setup
Technology Integration
- Platform Selection & Configuration
- Data Migration & System Integration
- Training & Adoption Management
- Performance Monitoring & Optimization
Performance Management Setup
- Metric Definition & Tracking
- Compensation Structure Adjustments
- Accountability & Review Processes
- Feedback & Improvement Mechanisms
Common Structural Challenges and Solutions
Communication Breakdowns
- Information Silos Solution: Centralized communication systems.
- Inconsistent Client Communication Solution: Clear contact and handoff protocols.
- Technology Gaps Solution: Standardize platforms with intelligent email parsing.
Role Confusion and Overlap
- Unclear Responsibility Boundaries Solution: Detailed role definitions and escalation procedures.
- Client Confusion About Contacts Solution: Clear contact guides and primary relationship managers.
- Duplicate Efforts and Conflicts Solution: Task assignment systems and unified platforms.
Scalability Issues
- Growth Bottlenecks Solution: Flexible structures accommodating new members.
- Quality Control Challenges Solution: Systematic quality checkpoints.
- Resource Allocation Difficulties Solution: Transparent allocation systems.
Technology Solutions for Structural Success
- Intelligent Email Parsing & Task Automation
- Integrated Communication Platforms
- Performance Tracking & Reporting
- Workflow Automation
Measuring Success: KPIs for Each Structure Model
Universal Metrics
- Transaction Volume & Revenue/Agent
- Client Satisfaction & Retention
- Cost/Transaction & Profit Margins
- Market Share & Competitive Position
Structure-Specific Metrics
- Hierarchy: Leadership development, succession readiness.
- Partnership: Decision speed, conflict resolution.
- Specialist: Cross-referral rates, collaboration effectiveness.
- Geographic: Territory performance, community engagement.
- Lifecycle: Phase conversion rates, handoff efficiency.
- Hybrid: Participation levels, resource utilization.
- Virtual: Collaboration effectiveness, culture maintenance.
Technology Performance Indicators
- Email Processing Efficiency
- System Adoption Rates
- Data Accuracy & Accessibility
- Workflow Optimization Success
Future-Proofing Your Team Structure
Emerging Trends & Technologies
- AI & Automation Impact
- Virtual Reality & Digital Platforms
- Predictive Analytics
- Client Experience Evolution
Adaptability & Evolution
- Structure Flexibility
- Continuous Improvement Processes
- Change Management
- Innovation Framework
Getting Started: Your Structure Selection Toolkit
Team Assessment Worksheet
- Current Structure Evaluation
- Strengths & Weakness Analysis
- Growth Opportunity Identification
- Resource & Capability Inventory
Model Comparison Framework
- Feature & Benefit Comparison
- Implementation Complexity Ratings
- Resource Requirement Assessments
- ROI & Timeline Projections
Implementation Roadmap Template
- Phase-Based Planning
- Milestones & Checkpoints
- Technology Rollout Scheduling
- Performance Monitoring & Adjustment
Conclusion: Structure as Competitive Advantage
The right team structure isn’t just an organizational tool—it’s a competitive weapon that enables superior client service, operational efficiency, and sustainable growth.
Key Success Principles:
- Alignment with Goals & Culture
- Implementation Excellence
- Technology Integration
- Continuous Evolution
- Performance Focus
As real estate continues evolving, teams that combine thoughtful design with intelligent workflow systems will dominate their markets. Those that integrate specialized expertise, systematic efficiency, and personal relationships will lead the future.
Want to see how intelligent email organization and workflow automation can support any team structure? Try DocJacket’s AI-powered transaction management system free for 30 days and discover how automated communication processing can eliminate administrative bottlenecks while improving coordination and client service across any organizational model.